“A bad process will beat a good person every time.” – W. Edwards Deming
Lean Six Sigma: A Unified Approach
In the realm of business methodologies, Lean Six Sigma stands as a potent combination of Lean and Six Sigma, synergizing their strengths to drive profound transformations and deliver impactful benefits across various dimensions:
- Elevated Profits
- Decreased Costs
- Streamlined Operational Efficiencies
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction
- Empowerment of Employees
Before immersing ourselves in the realm of Lean Six Sigma, it’s pivotal to grasp the essence of its foundational components:
Understanding Lean
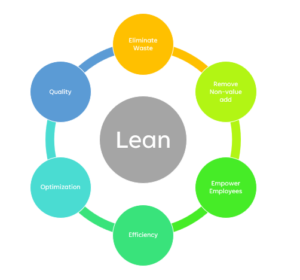
Originating from the Toyota Production System, Lean is a methodology dedicated to eradicating waste and non-value-added processes. By excising these inefficiencies, it crafts a value-centric approach characterized by:
- Meeting Precise Customer Needs
- Elimination of the Eight Wastes
- Delivery of a Near-Perfect Process
- Cultivation of a Continuous Improvement Mindset
- Empowerment of All Employees
- Flexibility and Agility in Operations
Emphasizing customer value and fostering an environment of perpetual process enhancement lie at the core of Lean principles.
Unpacking Six Sigma
Six Sigma represents a disciplined, data-driven methodology aimed at process enhancement by eliminating defects and minimizing process variations. Leveraging insights from process knowledge, data analytics, and statistics, Six Sigma fosters improvements resulting in tangible business outcomes:
- Augmented Operational Efficiency
- Increased Throughput
- Cost Savings
- Enhanced Revenue Streams
- Reduced Customer Churn
- Amplified Profit Margins
The amalgamation of Lean and Six Sigma births a powerhouse methodology known as Lean Six Sigma, wielding a formidable arsenal of tools that generate superior products, services, or processes. This convergence leads to heightened customer satisfaction, substantial cost savings, and amplified revenue streams.
While both Lean and Six Sigma share a common goal, their approaches to identifying waste differ. Lean focuses on non-value-added steps as the source of waste, while Six Sigma targets variation. However, their combination births an even more potent force, leveraging their unique insights.
Real-Life Illustration of Lean Six Sigma in Action
Consider the case of an international data company within the Talent Acquisition domain. Initially, it took an exorbitant 1.5 to 5 weeks to post a job opening, resulting in a loss of potential talent. The Lean Six Sigma Team meticulously identified several non-value-added elements and waste within the process:
- Excessive Meetings
- Redundant Validations
- Human Errors
- Cumbersome Forms
- Unnecessary Data Fields
- Outdated IT Systems
- Lack of System Integration
Addressing these root causes, the project implemented strategic improvements:
- Consolidating to One Kick-Off Meeting
- Introduction of a New IT System
- Implementation of Automated Progress Updates
- Creation of a Unified Global Form within the IT System
- Integration between Systems
- Implementation of Poka-Yoke (Mistake-Proofing) Measures
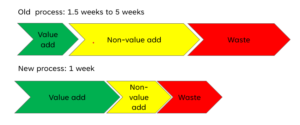
The outcome was remarkable: the Lean Six Sigma initiative slashed the cycle time from 1.5-5 weeks down to a single week, resulting in substantial cost savings of $250,000.
Ready to unlock the transformative potential of Lean Six Sigma and drive unparalleled efficiency in your business? Empower yourself and your team with the tools to revolutionize processes and achieve remarkable results. Take the first step toward mastering Lean Six Sigma methodologies by enrolling in our comprehensive training program today. Join us to embark on a journey towards operational excellence and sustainable success. Elevate your skills and amplify your impact! Sign up now and pave the way for a future of streamlined efficiency and remarkable growth
Learn more about our TRAINING Programs
Follow us on YouTube!
